RabbitMQ路由模式与主题模式
RabbitMQ 路由模式(Direct)介绍
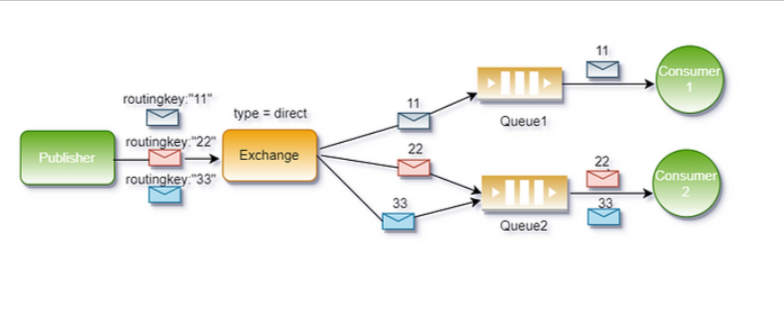
Direct模式是RabbitMQ中交换机(Exchange)的一种工作模式,通过精确匹配路由键(Routing Key)和绑定键(Binding Key),将消息路由到对应的队列。适用于需要根据特定规则精确分发消息的场景。
核心原理
- 生产者发送消息时指定一个路由键。
- Direct Exchange 将消息转发给所有绑定键(Binding Key)与路由键完全匹配的队列。
- 消费者监听特定队列,处理匹配的消息。
应用场景
- 日志分级处理
不同级别的日志(如 error、info)分发到不同队列,由消费者独立处理。 - 订单类型路由
根据订单类型(如 digital、physical)将消息路由到对应的业务处理服务。 - 消息分类通知
例如,将sms、email消息分发到不同的通知通道。
注意事项
● 精确匹配:路由键和绑定键需完全一致。
● 多队列绑定:若多个队列绑定相同键(如两个队列均绑定error),消息会同时分发到这些队列(类似广播)。
● 性能:Direct模式效率高,适合需要精确控制的场景,但不支持通配符(需使用Topic模式)。
1 | package com.lixiang.rabbitmq; |
1 | package com.lixiang.rabbitmq; |
1 | package com.lixiang.rabbitmq; |
RabbitMQ主题模式(TOPIC)
RabbitMQ 的主题模式(Topic Exchange)是一种支持基于消息路由键(Routing Key)进行灵活匹配的消息分发模式。它允许生产者发送带有特定路由键的消息,消费者通过绑定键(Binding Key)订阅符合规则的消息。
在主题模式中,路由键和绑定键可以包含多个单词,以点号(.)分隔,例如stock.usd.nyse或weather.europe.london。此外,绑定键支持两种通配符:
● *:匹配一个单词。
● #:匹配零个或多个单词。
工作原理
- 生产者发送消息时,指定一个路由键。
- 消息被发送到 Topic Exchange。
- Topic Exchange 根据绑定键的规则将消息路由到符合条件的队列。
○ 如果绑定键与路由键完全匹配,则消息会被路由到对应的队列。
○ 如果绑定键包含通配符,则会根据通配符规则进行匹配。
示例
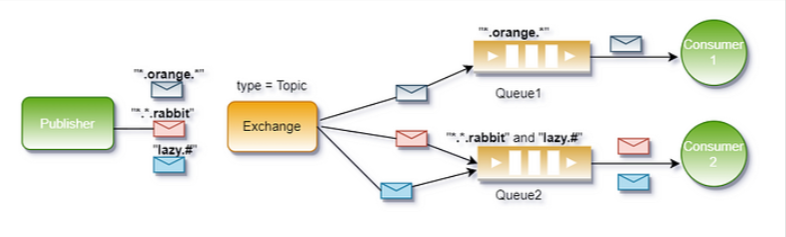
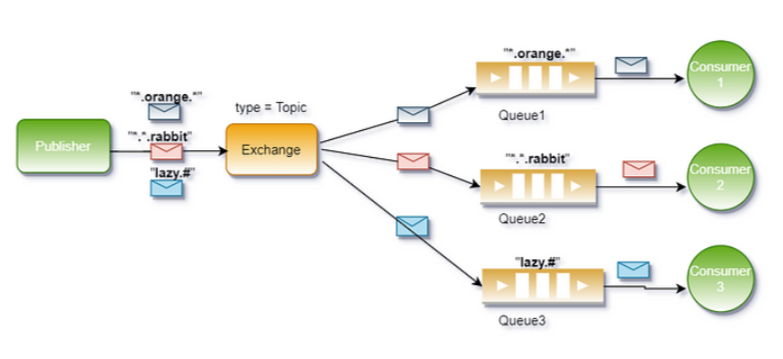
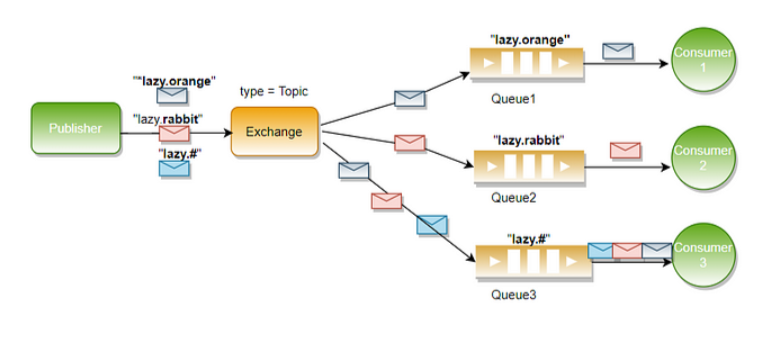
假设有一个Topic Exchange,以下是绑定键和路由键的例子:
● 绑定键:*.orange.*
○ 匹配路由键:quick.orange.rabbit、lazy.orange.elephant
○ 不匹配路由键:orange、quick.orange.male.rabbit
● 绑定键:lazy.#
○ 匹配路由键:lazy.orange.elephant、lazy.brown.fox、lazy
○ 不匹配路由键:quick.orange.rabbit
应用场景
主题模式适用于需要对消息进行多维度分类和灵活订阅的场景。以下是一些典型的应用场景:
- 日志系统:
○ 路由键可以表示日志的来源和级别,例如 app.error、db.warning。
○ 消费者可以根据不同的需求订阅特定类型的日志,例如 *.error 订阅所有错误日志。 - 事件驱动架构:
○ 在微服务架构中,不同服务之间通过消息通信。
○ 主题模式允许服务根据事件类型和子类型灵活订阅感兴趣的消息,例如 order.created、payment.failed。 - 物联网(IoT)数据处理:
○ 设备上报的数据可以用路由键标识设备类型和位置,例如 sensor.temp.zone1。
○ 数据处理模块可以根据绑定键订阅特定区域或特定类型的传感器数据。
主题模式(TOPIC)与直接模式(DIRECT)的区别
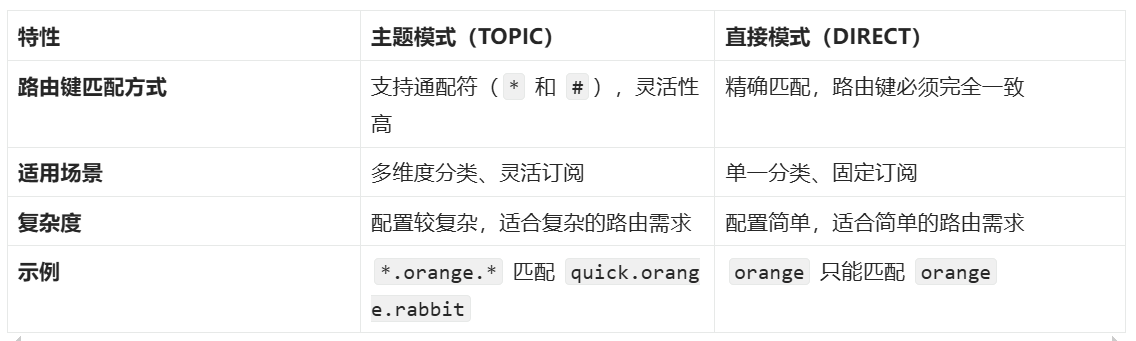
具体对比
- 灵活性:
○ DIRECT 模式要求路由键和绑定键完全匹配,适用于消息分类较为固定的场景。
○ TOPIC 模式支持通配符,允许更灵活的消息订阅,适合需要动态分类和多维度过滤的场景。 - 性能:
○ DIRECT 模式的匹配逻辑简单,性能较高。
○ TOPIC 模式需要解析通配符规则,可能带来一定的性能开销,但通常在现代硬件上影响较小。 - 使用场景选择:
○ 如果消息分类明确且固定(例如订单状态更新),建议使用 DIRECT 模式。
○ 如果需要支持多条件组合订阅(例如日志系统或事件驱动架构),建议使用 TOPIC 模式。
总结
RabbitMQ 的主题模式(TOPIC)是一种强大的消息路由机制,通过支持通配符的方式提供了极大的灵活性,适合需要多维度分类和动态订阅的场景。而直接模式(DIRECT)则更加简单高效,适用于分类明确且固定的场景。在实际应用中,应根据业务需求选择合适的模式,从而实现高效的系统设计。
1 | package com.lixiang.rabbitmq; |
1 | package com.lixiang.rabbitmq; |
1 | package com.lixiang.rabbitmq; |